Human-Autonomy Teaming (HAT)
Human-Autonomy Teaming (HAT) refers to collaborative systems in which human expertise is integrated with autonomous capabilities to achieve shared goals. Rather than being defined solely by the roles of humans or autonomous agents, HAT is characterized by the dynamic interactions and interdependencies within the team. Such teaming has the potential to significantly enhance performance, particularly in complex or uncertain environments where human judgment and machine precision can complement each other.
Research in HAT encompasses the development and evaluation of integrated human-autonomy systems across multiple scales. Key areas include cognitive engineering of autonomous agents, design methodologies for effective human-autonomy interaction, development of technological aids to support teaming, modeling and simulation of HAT behaviors, and rigorous testing and evaluation of team performance. Fundamental challenges also lie in the measurement and modeling of human-autonomy performance within engineered systems, requiring interdisciplinary approaches that span human factors, robotics, artificial intelligence, and systems engineering.
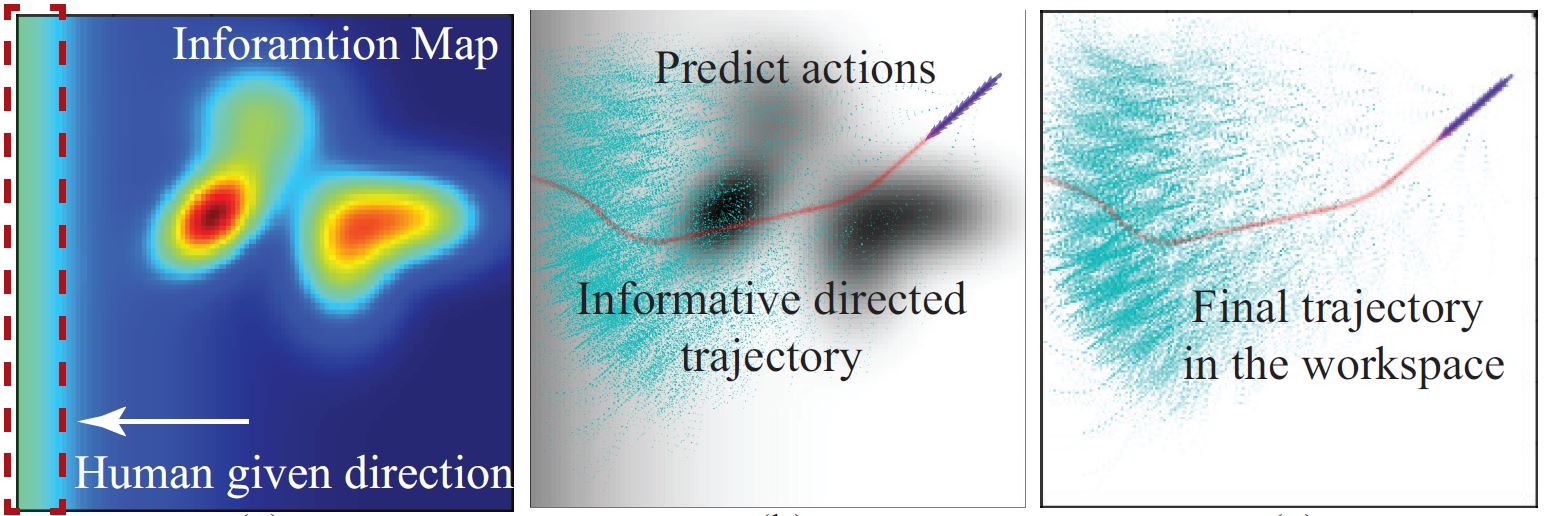
- Informed Sampling Space Driven Robot Informative Path Planning
- Human-Autonomy Teaming-Based Robot Informative Path Planning and Mapping Algorithms with Tree Search Mechanism
- Human Autonomy Teaming-Based Safety-Aware Navigation Through Bio-Inspired and Graph-Based Algorithms
- An Informative Planning-based Multi-Layer Robot Navigation System as Applied in a Poultry Barn
